Women Health: Practical Answers on BV and Uterine Lining Problems
About 1 in 3 women will face a vaginal infection at some point, and abnormal uterine bleeding affects many too. If you're trying to figure out whether your symptoms need a pill, a procedure, or a simple lifestyle change, this page pulls together clear, usable info on bacterial vaginosis (BV), metronidazole treatment, and overgrowth of the uterine lining (endometrial hyperplasia).
What is bacterial vaginosis and how metronidazole helps
Bacterial vaginosis happens when the normal balance of vaginal bacteria shifts and harmful bacteria take over. Common signs are thin, grayish discharge and a fishy smell, usually without strong pain. Metronidazole is one of the most prescribed antibiotics for BV. It comes as an oral pill or a vaginal gel. Typical oral treatment lasts seven days, and the gel is often used for five days. Take the full course even if symptoms improve quickly—stopping early raises the chance it comes back.
Watch for side effects like nausea, a metallic taste, or mild stomach upset. Avoid alcohol while using metronidazole and for 48 hours after the last dose—mixing them can cause flushing, nausea, and headaches. If symptoms continue after treatment, your provider may recheck for other infections or consider a different antibiotic.
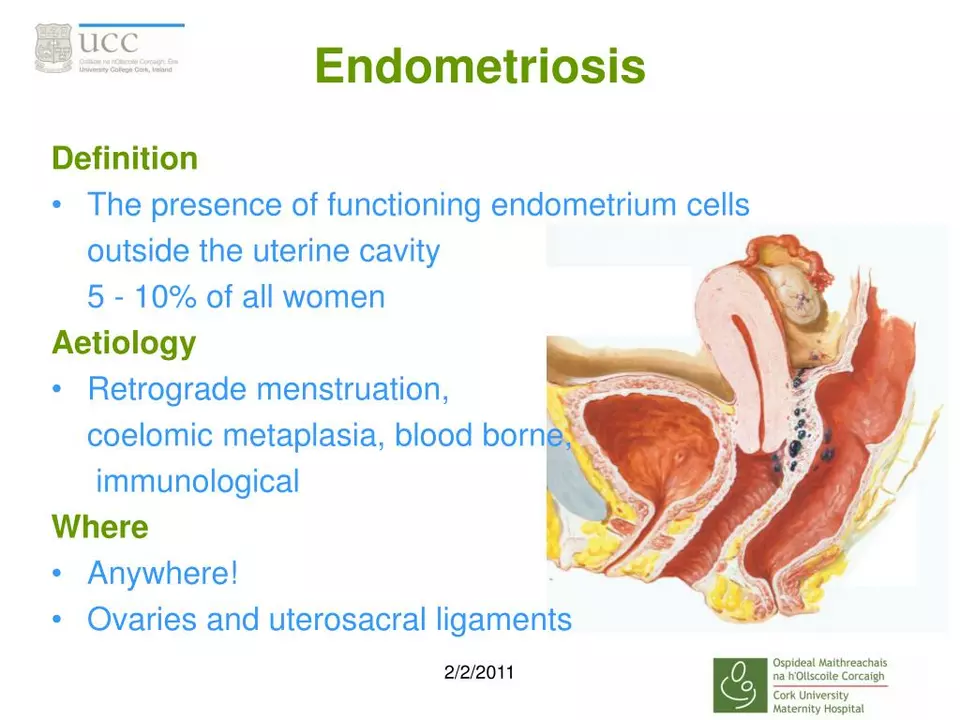
Uterine lining overgrowth: signs, causes, and options
Overgrowth of the uterine lining, called endometrial hyperplasia, usually shows up as heavy or irregular bleeding, spotting between periods, or bleeding after menopause. It’s often driven by excess estrogen without enough progesterone. Common risk factors include obesity, PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome), use of estrogen-only hormone therapy, and infertility issues.
Diagnosis typically uses a pelvic ultrasound and an endometrial biopsy to check the tissue. Treatment depends on the type and severity: some women respond to progesterone therapy (pills, IUD), others need a hysteroscopy to remove abnormal tissue, and in higher-risk cases a hysterectomy is discussed. If hyperplasia includes atypical cells, your doctor will recommend closer follow-up because the risk of progression to cancer is higher.
Simple prevention steps help lower risk: maintain a healthy weight, manage blood sugar if you have diabetes, and discuss balanced hormone options with your clinician. Regular check-ups and reporting unusual bleeding early make a big difference.
If you have heavy bleeding, persistent vaginal discharge with odor, pain, or bleeding after sex or menopause, see a healthcare provider. Quick evaluation can spare you bigger problems later and get you back to feeling like yourself sooner.